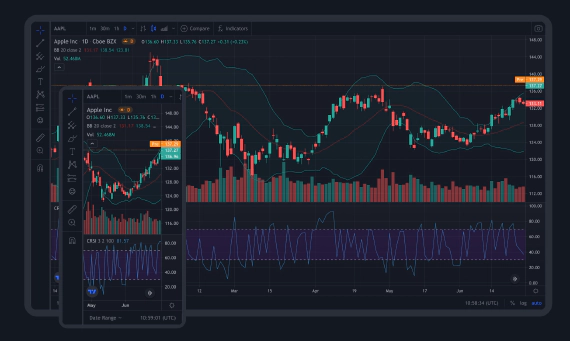
Trading view integration
At scalpers.sh uses trading view premium version as we believe they are true pioneer in financial charting system. …

Option trading offers a variety of strategies to profit from different market conditions. One such versatile strategy is the option straddle. The straddle is popular among traders who anticipate significant price movement but are uncertain about the direction. This article delves into the option straddle strategy, its mechanics, benefits, and risks.
An option straddle involves buying both a call option and a put option with the same strike price and expiration date on the same underlying asset. This strategy allows traders to profit from substantial price movements in either direction. The key is that the magnitude of the price movement must be sufficient to cover the cost of both options.
To implement a straddle, a trader purchases both a call and a put option on the same asset with identical strike prices and expiration dates. The total cost of this strategy is the combined premium paid for both options.
Suppose a trader believes that a stock currently trading at $100 will experience significant volatility but is unsure of the direction. The trader buys a call option with a strike price of $100 and a put option with the same strike price of $100, each costing $5. The total cost of the straddle is $10 (the sum of both premiums).
A straddle is particularly effective in situations where a trader expects significant volatility due to upcoming events such as:
While the straddle is a powerful strategy, traders might also consider other strategies depending on their market outlook and risk tolerance:
The option straddle is a versatile strategy that allows traders to profit from significant price movements in either direction. It is particularly useful in volatile markets or around major events that can drive substantial price changes. However, traders must be aware of the high initial cost and the impact of time decay on options premiums. As with any trading strategy, understanding the mechanics and risks is crucial for successful implementation.

At scalpers.sh uses trading view premium version as we believe they are true pioneer in financial charting system. …

youtube: https://youtu.be/k8d5p-Zwiyw?si=LiEDhHQxEuL_tmwc Get access to scalper.sh terminal in 2 minutes, by following …